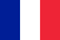
Onychomycosis - damage to the nails with a fungal infection. The disease occurs in 5-10% of the population, and among other nail lesions is about 30%.
The infection of the toenails is found mainly in public baths, saunas, pools. Scales with pathogenic mushrooms that fall into patients with onychomycosis fall on the floors, benches, bars, paths, carpets and waste. In high humidity conditions, mushrooms can not only continue for a long time, but also multiply, especially on uninvited wooden benches and grilles, which makes them an intense source of infection.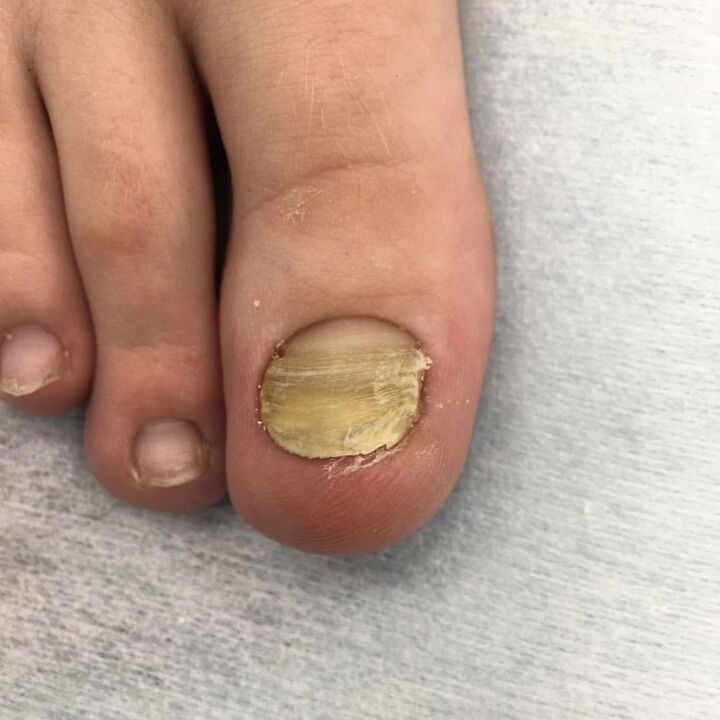
Often, onychomycosis is transmitted inside the family when using common shoes, towels, cloth, insufficient bath treatment after washing, as well as carpets and grilles in the bathroom. Damage to the nails of the hands usually occurs at the encounter of the hearth on the skin.
The onset of onychomycosis is facilitated by nail trauma, especially multiple (in athletes), impaired blood supply to the limbs, severe concomitant diseases (diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency conditions, blood disease).
Onychomycosis is common in persons who have long received antibacterial, corticosteroid and immunosuppressive therapy. The lesion of the nail plaque appears second: at first mushrooms affect the interdigital folds or sole, then the nails.
Three types of onychomycosis are distinguished all over the world:
With a smooth type of onychomycosis, only the color of the nails changes: in their extreme departments, spots and stripes appears, whose color varies from white to security. Gradually, the whole nail changes color, but maintaining shine and normal thickness.
With hypertrophic type, the color changes, the nail loses its luster, becomes dull, thickens and deforms, partially destroyed, especially by the sides. Often patients experience pain when walking. The typical nail fungus is characterized by a dumb brownish-gray color of the affected part of the nail, its thinning and rejection from the box; The bare area is covered with loose layers.
Local antifungal agents are ineffective with nail damage. Treatment with antifungal ointments, creams, solutions, varnishes must be preceded by removing the affected area of the nail mechanically or by the help of keratolytic plasters.
Mechanical removal consists in cutting or cutting with bites of affected nail fragments.
The use of keratolithic plasters in the treatment of onychomycosis allows you to soften the nail, which results in easily and painlessly removed from the surface of the nails with a blunt scalpel or scissors.
As a keratolithic agent, a medicine is used, which includes an ointment containing 1% antifungal agent and 40% urea. The ointment is applied to the surface of the nail and covered with the attached glue and dressing. After one day, the areas affected by onychomycosis are cleaned. The procedures are performed daily until the affected nails are completely removed. In the future, since the affected nail is removed, locals are used: antifungal varnishes. 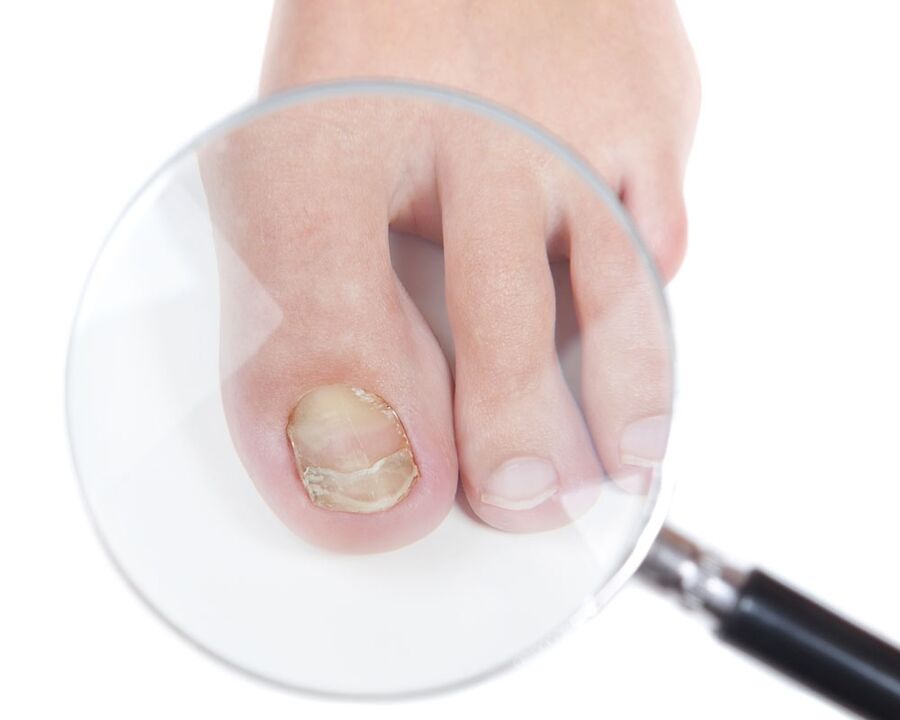
For the successful and safe treatment of onychomycosis, it is advisable to follow certain rules with systemic antifungal drugs.
First, the diagnosis should be reliable. The drug should not be prescribed if there is no laboratory confirmation.
After the diagnosis, it is necessary to carefully gather an allergic history. If at the same time, medicines or foods are detected that cause allergic reactions or other manifestations of intolerance, then their intake should be excluded.
For the period of treatment with systemic antifungals, it is advisable to limit the use of other medicines except Vital.
In order to prevent gastrointestinal disorders, it is recommended to exclude products that cause flatulence from food during treatment: black bread, legumes, milk, cabbage.
It is not a little important that is the choice of comfortable shoes both during treatment and after its completion. Often, improving the condition of the affected nail is clearly correlates with wearing non -traumatic shoes, as pollination of the tissues caused by shoes can cause exacerbation or distal on nail onychomycosis. Before you begin treatment, it is advisable to conduct a test of indicators for general and biochemical blood tests.
Control examinations should be carried out for the first time after 2 weeks, then 1 time per month. Control microscopy - 6 months after the end of treatment. Identification of the mycelium of pathogenic mushrooms serves as an indication of a second course of treatment with pre -surgical removal of the affected nails.
Despite the high rate of treatment for patients with onychomycosis using therapeutic agents, therapy with these drugs does not exclude the use of topical antifungal drugs. The combination with conservative and surgical nail removal reduces the time to take systemic antibacterial agents and increases the effectiveness of treatment.